Cryptography is the practice of writing or solving codes to keep information secure. It is used to protect digital data from unauthorized access and is used in various industries such as banking, healthcare, and government sectors as well as in everyday online activities. This article provides an in-depth guide to cryptography, including types, applications, examples, and its characteristics. Let’s start without any delay.
Introduction to Cryptography
Cryptography is made of two words ‘crypto’ which means hidden and ‘graphy’ which means writing or drawing. It refers to a secret form of writing or text which is in hidden form. It is a science and art of transforming messages to make them secure and immune to attack. It is essential for maintaining data security in the digital world. Cryptography in cyber security means securing communications, data, and other information from malicious attacks, data breaches, and other cyber threats.
Definition: Cryptography is a branch of science that deals with the practice of encoding data to protect its privacy, integrity, and authenticity using algorithms. It is a process of converting plaintext into ciphertext which is called encryption, then changing the ciphertext into plain text called decryption.
Some of the c-graphy examples include time stamping, electronic money, disk encryption, and online messages including WhatsApp and email.
What are the Types of Cryptography?
Talking about its types, it is divided into two main types: symmetric key and asymmetric key. Symmetric key cryptography is where the sender and receiver of the message both use the same key to encrypt and decrypt the message, while asymmetric key cryptography involves two different keys, one for encryption and one for decryption.
- Symmetric cryptography (or secret key cryptography): It is also known as private key cryptography or private key encryption. Here, only the private key is used to convert the plain text into cipher text and then the cipher text into plain text.
- Asymmetric cryptography (or public key cryptography): It is also known as public key encryption where the public key is used to convert the plain text into cipher text and the private key is used to convert the encrypted cipher text into plain text.
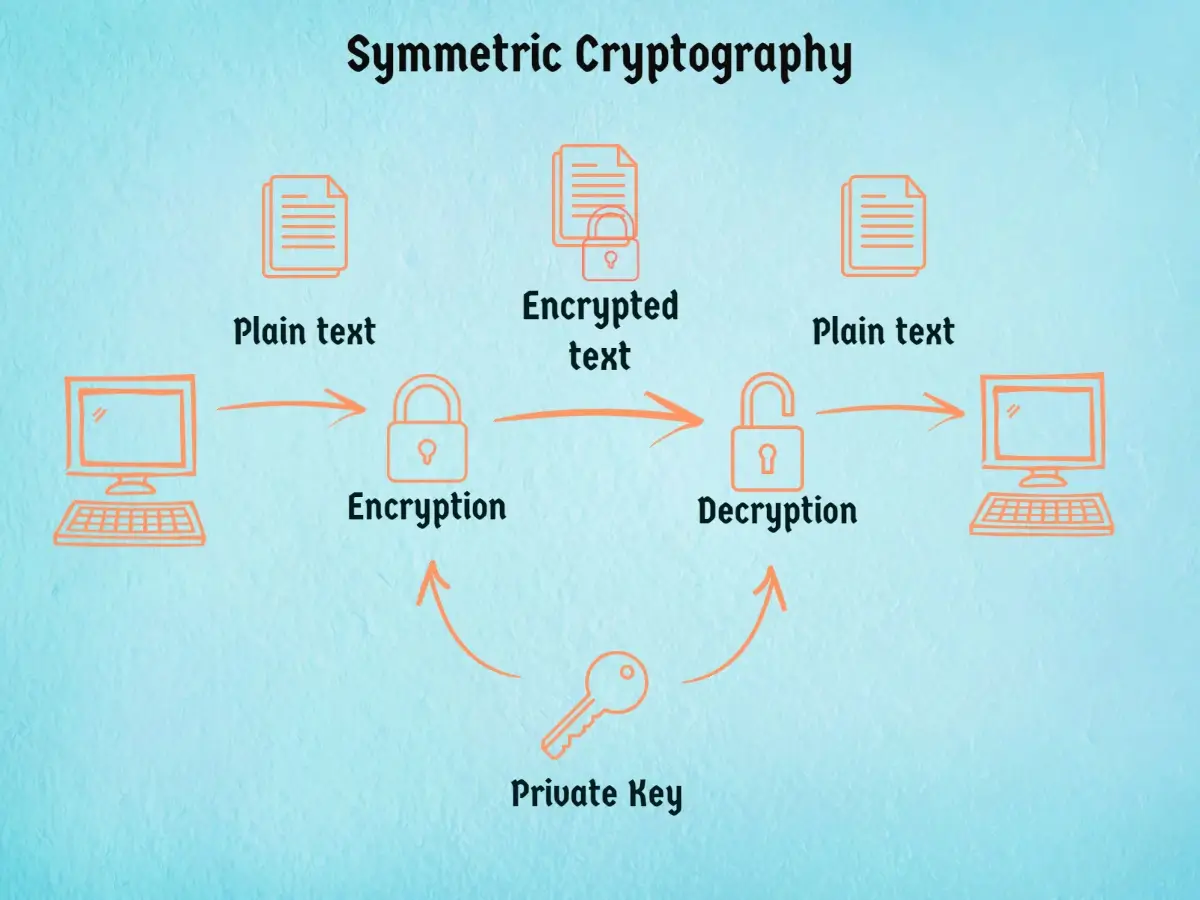
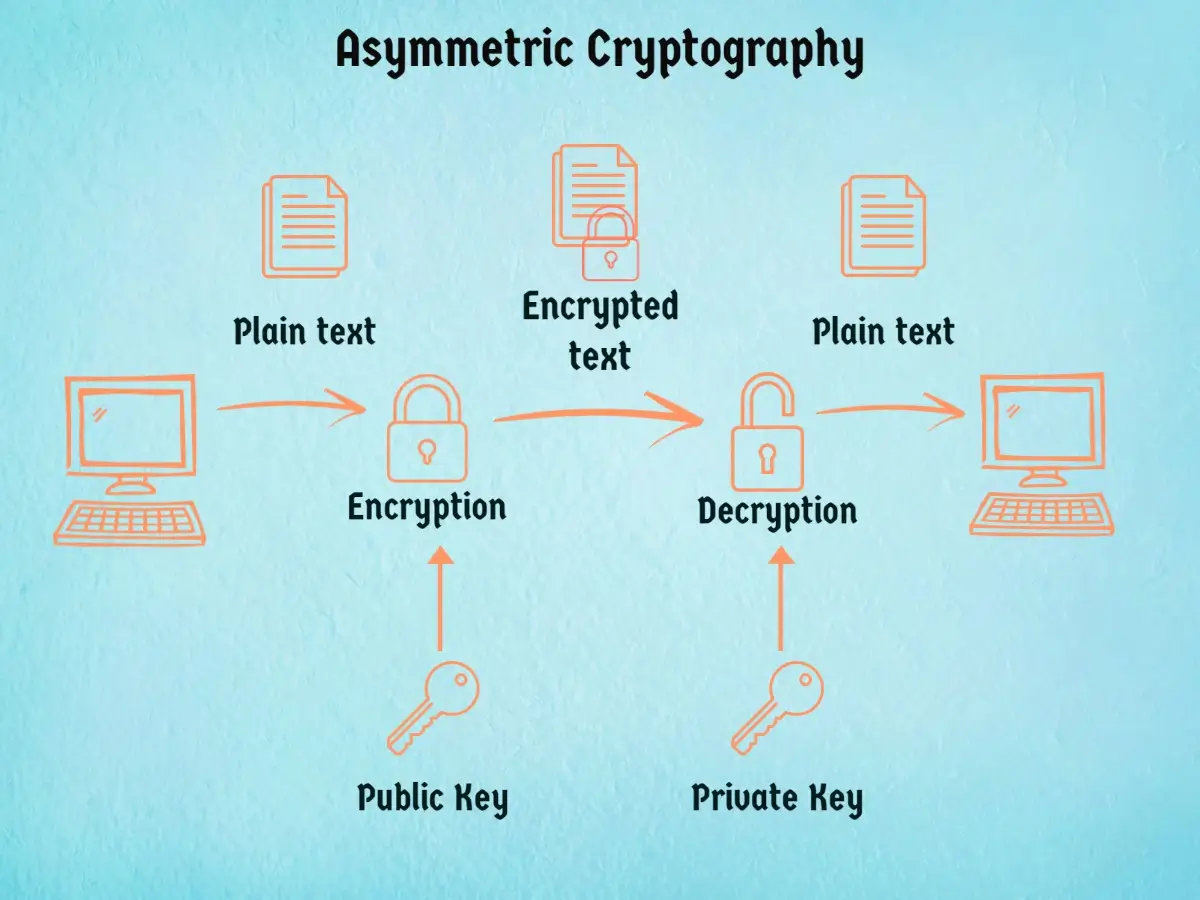
Let’s see the difference table of symmetric and asymmetric encryption to understand it better.
| Features | Symmetric Cryptography | Asymmetric Cryptography |
|---|---|---|
| Key Management | Requires only one key (Private Key). | Requires two keys (public and private). |
| Key Distribution | Both parties must securely share the same key. | Public key can be distributed to anyone. |
| Security | Security relies on the size of the key and secrecy of the key. | Security relies on the mathematical difficulty of the algorithm and the size of the key. |
| Speed | Fast encryption and decryption. | Slow encryption and decryption. |
| Use Cases | Confidentiality of data, message integrity. | Digital signatures, key exchange, secure data transmission. |
Other types of cryptography include:
- Hash functions (e.g. SHA-256, MD5)
- Digital signatures
- Steganography (hiding information in plain sight)
- Stream ciphers
- Block ciphers
Applications of Cryptography
Some of its common applications are:
- Digital currency
- E-commerce
- Military operations
- Authentication/digital signature.
- Timestamping
- Online transactions
It is also used in protecting data stored on servers, in the cloud, and on user devices. After discussing the application areas, let’s move to its characteristics and features.
Features and Characteristics of Cryptography
There are 5 basic features of cryptography which are as follows:
- Confidentiality: Ensures the protection of the information from unauthorized access.
- Integrity: Protects against unauthorized alteration of data.
- Non-repudiation: Prevents the sender from denying having sent the message.
- Authentication: Verifies the identity of the sender and receiver.
- Scalability: The system can easily handle small as well as large amounts of data.
In the digital age, c-graphy has become an essential tool for protecting data and communications. However, it also has weaknesses and can be exposed to various attacks.
Types of Attacks in Cryptography
Cryptographic attacks are methods used to compromise the security of encrypted data. Some common attacks include.
- Passive Attack: The goal of passive attack is to only obtain unauthorized access to the information.
- Active Attack: It involves changing the information by conducting some operations and processes on the information.
Some other types of attacks:
- Brute force attack: It is the most common attack where the intruder tries every possible combination of keys to find the right one.
- Man-in-the-middle attack: This is a practice of intercepting and altering communications between two parties.
- Denial of Service (DoS): It is an attempt to make a network resource unavailable to its intended users by overwhelming it with traffic.
- Collision attack: Finding two different input values that produce the same output value in a hash function.
- Dictionary attack: The practice of using a list of words to guess the key or password.
These are some of the most common types of attacks in c-graphy. To prevent these attacks, it’s important to use secure encryption algorithms and key management practices.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, cryptography is a technique for secure communication and information protection by encoding messages in such a way that only authorized parties can read them. There are various types of cryptography including symmetric-key cryptography, asymmetric-key cryptography, and hash functions. These techniques have various applications in fields such as military, finance, and internet security, among others. C-graphy plays a crucial role in maintaining the confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity of information in today’s digital age.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the 4 principles of cryptography?
Ans. The 4 principles are-
- Confidentiality
- Integrity
- Availability
- Authentication
2. What are the three major components of cryptography?
Ans. The three major components are Encryption, Decryption, and Key.
- Encryption: Transforming plaintext into ciphertext.
- Decryption: Transforming ciphertext back into plaintext.
- Key: Information used to encrypt/decrypt data.

Ankit Roy is a professional Technical Content Developer, Freelancer, and blogger. He holds a Masters’s degree in Computer Science and has worked as a Digital Marketing Strategist. With a deep understanding of technology trends like AI, ML, Big Data, Neural Networks, Network Infrastructure, etc., Ankit is able to communicate complex technical concepts in a clear and concise manner. He is a regular contributor to several websites and has authored numerous technical guides and instructional materials. In his free time, Ankit enjoys tinkering with new technologies and staying up-to-date with the latest developments in the field.